Technical Information
What is Rubber?
Rubber is a flexible substance produced from the sap (latex) of some tropical plants or from petroleum and natural gas. The one produced from the sap of trees is called natural rubber, and the one produced from petroleum products is called synthetic rubber. Both types are versatile substances. Items made of rubber are generally referred to as tyres.
Rubber is a durable, flexible material obtained from rubber tree, which has a great place in today’s industry. The rubber tree gets its name from ‘kauchi’, which means weeping tree in the Indian language. Seeing that a white, sticky and milky liquid was flowing from the tree, the locals dried it over time and started to make toy balls.
Over 15 million tons of rubber are produced annually all over the world; about a third of this is natural rubber. Due to the demand for natural rubber, synthetic rubber was obtained by the Germans in the 1900s in order to obtain cheap and abundant rubber, and thus many types of rubber emerged. When natural rubber is repeatedly stretched many times, it almost returns to its original dimensions. This feature distinguishes rubber from synthetic rubber and all other materials containing substances such as rubber.
Rubber, which is found in products such as shoes, raincoats, buttons, combs and belts that we use in our daily lives, is also widely used in car tires. It is a very important product due to its softness, durability, adhesiveness, water and air tightness, and it is used extensively in areas such as insulation and isolation as it does not conduct electricity.
Today, rubber is used as widely as wood and these advantages make this material perfect for tire production, largely due to its beneficial properties such as strength, longevity, water resistance and heat resistance. In fact, a large percentage of rubber production is in the automotive industry. Rubber comes in a wide variety of colors, styles, and textures and is extremely diverse.

How Is Rubber Formed?
The rubbery sap of the plant is called “latex”. Since latex is found in the inner part of the bark, the bark is slit in a V shape and the liquid is poured out. The resulting liquid is then taken into a shallow bowl and formic acid is added. Latex coagulates after 10-30 minutes. The coagulated latex becomes an elastic dough. Then rolling is done between the two rollers to allow excess water to be expelled.
After rolling, it is rinsed and dried on hangers in order to completely remove the formic acid. The latex that waits here for about 5 hours dries and gains a harder and stronger structure. It also darkens in color. After this process, the product is thoroughly cleaned by entering the brush washers.
The product, which is then taken to the shelves, is kept in brick ovens for 45 days in smoke. The reason for keeping it in the smoke is to prevent mold formation during this period. The rubber obtained at the end of 45 days is divided into classes, stacked on top of each other as leaves, pressed in order to occupy less space, and taken to warehouses.
Material Properties
The milky white liquid in the bark of the rubber tree is called “Latex”. Rubber is obtained from 30-40% of the collected liquid. Since natural rubber has a regular structure, its physical properties are positively affected. Another important feature of natural rubber is its smoothing under load and tension. Due to this feature, the breaking strength values increase even if there is no reinforcing filler in its structure.
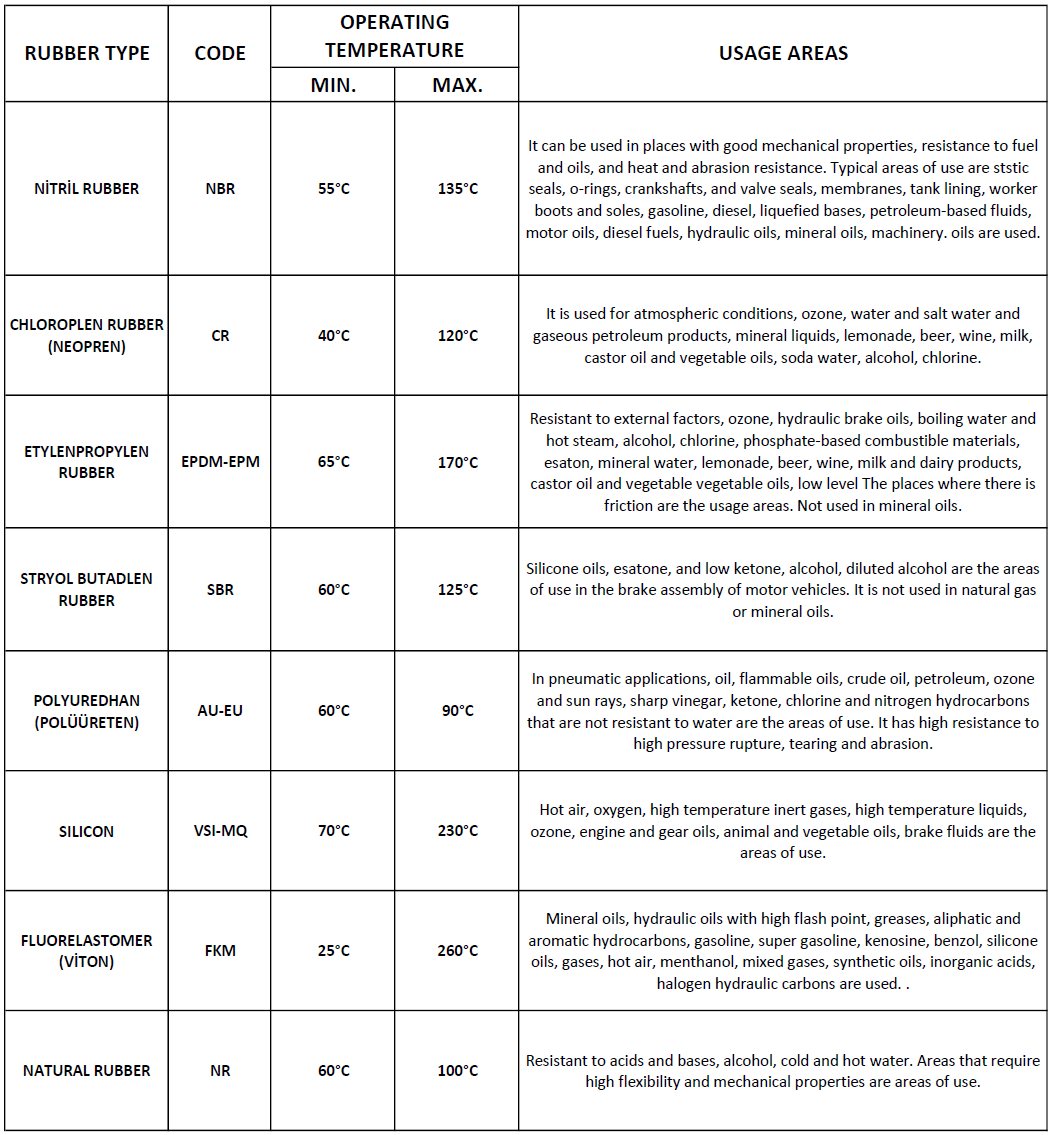
The operating temperature is between -60°C and 90°C.
Physical Properties:
High breaking strength
High tear strength
High raw rubber strength
High elasticity values
High dynamic values
High permanent deformation values
Usage Environment:
Aqueous environments with low temperatures
Glycol based oils
Usage Area:
Mechanical parts
Vibration and shock damping parts
Horoscope
Vibration damping connections
Engine parts
Shoe Sole
Hoses
Conveyor belts
Floor covering
Sponge
Adhesives
It is the most used, low cost synthetic rubber in the world. The structure of the mixture is irregular. It can be used instead of natural rubber.
The operating temperature is between -50°C and 100°C.
Physical Properties:
easy to process
Can be processed in a short time
It is suitable for processing by extrusion method.
Low elasticity values
High wear resistance
High aging strength
Usage Environment:
Solvent chemicals
Glycol based brake oils
Bases
Usage Area:
Vehicle tires
Light-coloured technical materials
Extrusion materials
Cable and electrical materials
Brake and clutch pads
Transparent tapes
Adhesives
Dynamic parts (V-belts)
It is used in the production of light materials due to its low density. It offers the opportunity to make low-cost mixes. Good physical properties at high additive ratio, low specific gravity and rapid mixing, extrusion and vulcanization properties are among the production advantages.
It can be used between -40°C and 150°C.
Usage Environment:
Aqueous and concentrated Acids
Alkalis
Silicone liquids
Hot water and steam
Phosphate ester based non-Flammable Hydraulic fluids
Usage Area:
Insulator material in high voltage cables
Door and glass insulation
Radiator and heater hoses
Bellows and gaskets Conveyor belts for white Goods and automotive
Insulation for water and chemical tanks
It is formed as a result of mixing Acrylonitrile and Butadiene monomers with the help of auxiliary additives. The ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture determines the properties of the material. Generally, the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture varies between 18% and 50%. Acrylonitrile provides polar properties to the mixture, reducing the solubility against hydrocarbons.
As the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture increases; The resistance of the material to oils, fuels, lubricants, greases and gases increases. Density hardness increases the rate of cooking. The workability of the mixture becomes easier. Its mechanical properties improve. Its elasticity coefficient, permanent permanence value, resistance to aging, fatigue and abrasion increases, and its life is extended.
As the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture decreases; The strength of the material at low temperatures decreases. Permanent deformation values deteriorate. Its elasticity is reduced. It becomes difficult to manufacture. It is a material that is mostly used for general purposes, preferred in the manufacture of sealing elements, and offers a cost-price advantage according to the functions it performs.
It can be used between -40°C and 100°C.
Usage Area:
Sealing elements
Pneumatic hoses
Connectors
Conveyor belts
Cylinder coating
Worker clothes and boots
Rubber plates and seals
Coupling, membrane, gasoline, oil and Hydraulic hoses
Unlike polymer rubbers, it consists of Silicon and Oxygen bond systems. Although the forces between the bonds are weak, it has a stable structure. The bond structures formed are expressed with the letter “Q”. Their nomenclature varies according to the auxiliary materials used during preparation. If the Silicone Rubber Mixture is prepared with Methyl (CH – Saturated Hydrocarbon), “MQ”, if it is prepared with Methyl Vinyl (Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbon), “VMQ”, if it is prepared with Phenyl Methyl (Organic Hydrocarbon and Saturated Hydrocarbon), “PMQ”. is expressed. Its resistance to ultraviolet rays, ozone and external factors, air and humidity is excellent.
It can be used between -50°C and 200°C.
Usage Environment:
High ultraviolet resistance
Superior ozone resistance
Resistant to external factors
Weather and moisture resistance
Superior insulation properties
It is fire resistant
Aging resistance is very good
It is long lasting
Shows high strength even underground
Can be processed transparently
Elastic properties are very good
can be easily painted
not poisonous
Physiologically harmless
It is an expensive material
Usage Area:
Cable, cable end, insulators and keys
Spark plug wires and caps
Radiator hoses and insulation elements
Insulated brake diaphragms
Baby pacifiers
Gas masks
Sealing gaskets for ovens
Sealing gaskets for refrigerator cabinets
Sealing gaskets for ozone units and systems)
High temperature, oil and fuel durability properties are very good. It can operate at high temperatures. It has low swelling property. Resistant to aromatic hydrocarbons, oils, greases, chemicals, acids, petroleum oils and solvents. It has high resistance to oxygen and ozone. It is resistant to burning; does not catch fire. Gas permeability is low. It is a difficult and expensive rubber material to process. It is not suitable for contact with nutrients.
It can be used between -30°C and 250°C.
Usage Environment:
Aromatic hydrocarbons
Fuels
Oils
Greases
Acids
Petroleum oils
Solvents
Usage Area:
Aerospace industry
Automotive industry
Cylinder coating
HNBR; while maintaining its excellent resistance to engine oils, acidic gas, amine/oil mixtures, oxidized fuels and machine oils; It fills the gap between NBR, EPDM and FKM(Viton) where high temperature conditions require high tensile strength.
Fully saturated NBR grades can crosslink with peroxides. The peroxide cross-links formed along this double bond increase the thermal stability and oxidation balance.
Vulcanizates; It provides the highest hot air and hot oil resistance that can be obtained with NBRs, oxidative and ozone decomposition resistance, resistance to oils containing sulfur, resistance to oil additives containing sulfur and nitrogen (nitrogen), including hydrogen sulfide, and industrial chemicals.
The material is characterized by high mechanical strength and enhanced wear resistance.
It is used between -30°C and 150°C.
ACM is obtained from the copolymerization of acrylic esters with monomers. Acrylic esters used; ethyl acrylate and/or butyl or octyl acrylate is ethylmethoxy or ethyloxy acrylate. These copolymers are very resistant to oil, heat, aging and ozone.
Tensile properties of acrylic rubbers are not as good as NR and NBR. Especially the new generation ACMs can work up to 1000 hours at around 160-170°C. But they show softening at high temperatures.
ACM vulcanizates are more resistant to swelling in animal, vegetable and mineral oils than other rubbers, with the exception of FKM, which decreases with increasing temperature. Its resistance to chemicals is not very good either. Its dry running properties are bad, it is not suitable for use in low temperature and water.
More than 90% of ACM products are used in the automotive industry. They are generally used as shaft seals in crankshafts, automatic and differential transmissions, as well as in o-rings, valves and oil hoses. Although its high price overshadows its other features, fluoro elastomer (FKM) is preferred in many applications.
It is used between 160°C and 170°C.
Polar characteristics are good. It is resistant to many oils and burning. It has low gas permeability. It has strong adhesion to textile and metal materials. Wear resistance is very good. It has superior mechanical properties.
The operating temperature is between -20°C and 120°C.
Physical Properties:
Resistant to oils
Resistant to weather and ozone
water resistant
Resistant to chemicals
Resistant to acids
Usage Area:
Parts at risk of burning
V belts
Rubber bellows
Vibration damping elements
Diving suits
High pressure hydraulic and brake hoses
Gaskets
The milky white liquid in the bark of the rubber tree is called “Latex”. Rubber is obtained from 30-40% of the collected liquid. Since natural rubber has a regular structure, its physical properties are positively affected. Another important feature of natural rubber is its smoothing under load and tension. Due to this feature, the breaking strength values increase even if there is no reinforcing filler in its structure.
The operating temperature is between -60°C and 90°C.
Physical Properties:
High breaking strength
High tear strength
High raw rubber strength
High elasticity values
High dynamic values
High permanent deformation values
Usage Environment:
Aqueous environments with low temperatures
Glycol based oils
Usage Area:
Mechanical parts
Vibration and shock damping parts
Horoscope
Vibration damping connections
Engine parts
Shoe Sole
Hoses
Conveyor belts
Floor covering
Sponge
Adhesives
It is the most used, low cost synthetic rubber in the world. The structure of the mixture is irregular. It can be used instead of natural rubber.
The operating temperature is between -50°C and 100°C.
Physical Properties:
easy to process
Can be processed in a short time
It is suitable for processing by extrusion method.
Low elasticity values
High wear resistance
High aging strength
Usage Environment:
Solvent chemicals
Glycol based brake oils
Bases
Usage Area:
Vehicle tires
Light-coloured technical materials
Extrusion materials
Cable and electrical materials
Brake and clutch pads
Transparent tapes
Adhesives
Dynamic parts (V-belts)
It is used in the production of light materials due to its low density. It offers the opportunity to make low-cost mixes. Good physical properties at high additive ratio, low specific gravity and rapid mixing, extrusion and vulcanization properties are among the production advantages.
It can be used between -40°C and 150°C.
Usage Environment:
Aqueous and concentrated Acids
Alkalis
Silicone liquids
Hot water and steam
Phosphate ester based non-Flammable Hydraulic fluids
Usage Area:
Insulator material in high voltage cables
Door and glass insulation
Radiator and heater hoses
Bellows and gaskets Conveyor belts for white Goods and automotive
Insulation for water and chemical tanks
It is formed as a result of mixing Acrylonitrile and Butadiene monomers with the help of auxiliary additives. The ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture determines the properties of the material. Generally, the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture varies between 18% and 50%. Acrylonitrile provides polar properties to the mixture, reducing the solubility against hydrocarbons.
As the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture increases; The resistance of the material to oils, fuels, lubricants, greases and gases increases. Density hardness increases the rate of cooking. The workability of the mixture becomes easier. Its mechanical properties improve. Its elasticity coefficient, permanent permanence value, resistance to aging, fatigue and abrasion increases, and its life is extended.
As the ratio of acrylonitrile in the mixture decreases; The strength of the material at low temperatures decreases. Permanent deformation values deteriorate. Its elasticity is reduced. It becomes difficult to manufacture. It is a material that is mostly used for general purposes, preferred in the manufacture of sealing elements, and offers a cost-price advantage according to the functions it performs.
It can be used between -40°C and 100°C.
Usage Area:
Sealing elements
Pneumatic hoses
Connectors
Conveyor belts
Cylinder coating
Worker clothes and boots
Rubber plates and seals
Coupling, membrane, gasoline, oil and Hydraulic hoses
Unlike polymer rubbers, it consists of Silicon and Oxygen bond systems. Although the forces between the bonds are weak, it has a stable structure. The bond structures formed are expressed with the letter “Q”. Their nomenclature varies according to the auxiliary materials used during preparation. If the Silicone Rubber Mixture is prepared with Methyl (CH – Saturated Hydrocarbon), “MQ”, if it is prepared with Methyl Vinyl (Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbon), “VMQ”, if it is prepared with Phenyl Methyl (Organic Hydrocarbon and Saturated Hydrocarbon), “PMQ”. is expressed. Its resistance to ultraviolet rays, ozone and external factors, air and humidity is excellent.
It can be used between -50°C and 200°C.
Usage Environment:
High ultraviolet resistance
Superior ozone resistance
Resistant to external factors
Weather and moisture resistance
Superior insulation properties
It is fire resistant
Aging resistance is very good
It is long lasting
Shows high strength even underground
Can be processed transparently
Elastic properties are very good
can be easily painted
not poisonous
Physiologically harmless
It is an expensive material
Usage Area:
Cable, cable end, insulators and keys
Spark plug wires and caps
Radiator hoses and insulation elements
Insulated brake diaphragms
Baby pacifiers
Gas masks
Sealing gaskets for ovens
Sealing gaskets for refrigerator cabinets
Sealing gaskets for ozone units and systems)
High temperature, oil and fuel durability properties are very good. It can operate at high temperatures. It has low swelling property. Resistant to aromatic hydrocarbons, oils, greases, chemicals, acids, petroleum oils and solvents. It has high resistance to oxygen and ozone. It is resistant to burning; does not catch fire. Gas permeability is low. It is a difficult and expensive rubber material to process. It is not suitable for contact with nutrients.
It can be used between -30°C and 250°C.
Usage Environment:
Aromatic hydrocarbons
Fuels
Oils
Greases
Acids
Petroleum oils
Solvents
Usage Area:
Aerospace industry
Automotive industry
Cylinder coating
HNBR; while maintaining its excellent resistance to engine oils, acidic gas, amine/oil mixtures, oxidized fuels and machine oils; It fills the gap between NBR, EPDM and FKM(Viton) where high temperature conditions require high tensile strength.
Fully saturated NBR grades can crosslink with peroxides. The peroxide cross-links formed along this double bond increase the thermal stability and oxidation balance.
Vulcanizates; It provides the highest hot air and hot oil resistance that can be obtained with NBRs, oxidative and ozone decomposition resistance, resistance to oils containing sulfur, resistance to oil additives containing sulfur and nitrogen (nitrogen), including hydrogen sulfide, and industrial chemicals.
The material is characterized by high mechanical strength and enhanced wear resistance.
It is used between -30°C and 150°C.
ACM is obtained from the copolymerization of acrylic esters with monomers. Acrylic esters used; ethyl acrylate and/or butyl or octyl acrylate is ethylmethoxy or ethyloxy acrylate. These copolymers are very resistant to oil, heat, aging and ozone.
Tensile properties of acrylic rubbers are not as good as NR and NBR. Especially the new generation ACMs can work up to 1000 hours at around 160-170°C. But they show softening at high temperatures.
ACM vulcanizates are more resistant to swelling in animal, vegetable and mineral oils than other rubbers, with the exception of FKM, which decreases with increasing temperature. Its resistance to chemicals is not very good either. Its dry running properties are bad, it is not suitable for use in low temperature and water.
More than 90% of ACM products are used in the automotive industry. They are generally used as shaft seals in crankshafts, automatic and differential transmissions, as well as in o-rings, valves and oil hoses. Although its high price overshadows its other features, fluoro elastomer (FKM) is preferred in many applications.
It is used between 160°C and 170°C.
Polar characteristics are good. It is resistant to many oils and burning. It has low gas permeability. It has strong adhesion to textile and metal materials. Wear resistance is very good. It has superior mechanical properties.
The operating temperature is between -20°C and 120°C.
Physical Properties:
Resistant to oils
Resistant to weather and ozone
water resistant
Resistant to chemicals
Resistant to acids
Usage Area:
Parts at risk of burning
V belts
Rubber bellows
Vibration damping elements
Diving suits
High pressure hydraulic and brake hoses
Gaskets